CSS Property Margin – Outer Spacing of a Box
The CSS margin property is used to set the outer spacing of an element relative to its parent or to adjacent elements. This means that margin will push the other elements away from it.
Margin is the shorthand property for the four properties
| margin-top | space to the top |
| margin-right | space to the right |
| margin-bottom | space to the bottom |
| margin-left | space to the left |
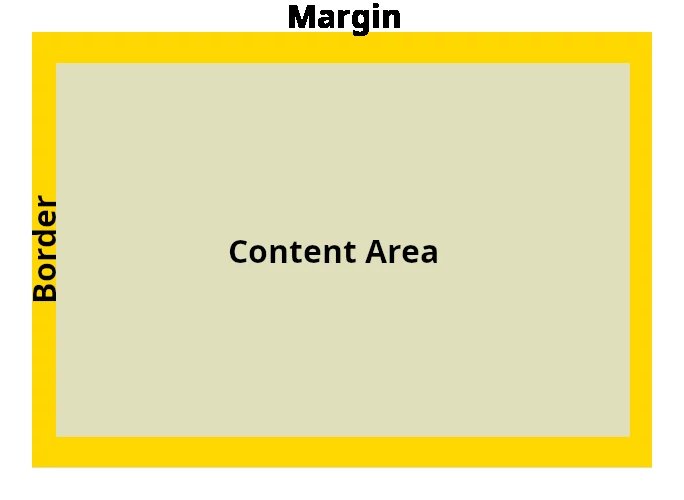
| Description | Possible Values | Default Value | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| outer space (white space) | length in px or em percentage auto initial inherit |
0 | box model spacing |
The value shown in orange is the standard use of the CSS margin property.
-
The margin property is used to create space around the element outside of any defined borders. The margins for each of the four sides (top, right, bottom, left) can be specified individually. They are usually given in px, em, or as a percentage. The space around the element is also called white space.
-
margin accepts 1, 2, 3, or 4 values to define the spacing used for each of the four sides.
-
One Value
The value applies to each of the four sides. -
Two Values
The first value specifies the vertical spacing of the element and applies to margin-top (above) and margin-bottom (below).The second value specifies the horizontal spacing of the element and applies to margin-left (left side) and margin-right (right side).
-
Three Values
The first value specifies the vertical spacing above the element and applies to (margin-top).The second value specifies the horizontal spacing of the element and applies to margin-left (left side) and (margin-right) (right side).
The third value specifies the vertical spacing below the element and applies to (margin-bottom).
-
Four Values
The values are given clockwise, starting with the spacing above the element, i.e.:The first value specifies the spacing above the element and applies to margin-top.
The second value specifies the right side spacing and applies to margin-right.
The third value specifies the spacing below the element and applies to margin-bottom.
The fourth value specifies the left side spacing and applies to margin-left.
-
-
Margin doesn't affect the width or height of the HTML element. However, the total space required is the width respectively height of the Content Area plus margin.
-
Negative values for margin are allowed, but they are usually not a good idea since this can result in overlapping areas.
-
The auto value is a special case of outer spacing. When this value is set, the web browser itself determines the spacing. The most common use of the auto value is to center a block level element.
Define Outer Spacing for HTML Elements with margin
div {
/* outer spacing: 1em vertical, 2em horizontal */
margin: 1em 2em;
/* background: antiqueWhite */
background: #faebd7;
/* border: gold */
border: 1px solid #ffd700;
}
/* define paragraph */
p {
/* background: paleSpring */
background: #dfdfbc;
/* text color: darkGrey */
color: #404040;
/* border: darkRed */
border: 1px solid #dd0000;
}Using Outer Spacing for HTML Elements with margin
<div>
<p>In contrast to previous websites, for example, we no longer need to code two different websites one for Internet Explorer and one for other browsers. Now one page that is suitable for all browsers is sufficient. The page is also suitable for printing or for displaying on a smartphone. Please note: one page is suitable for all browsers and all devices.</p>
</div>
Outer Spacing for HTML Elements
In contrast to previous websites, for example, we no longer need to code two different websites one for Internet Explorer and one for other browsers. Now one page that is suitable for all browsers is sufficient. The page is also suitable for printing or for displaying on a smartphone. Please note: one page is suitable for all browsers and all devices.